Dyes & Pigments
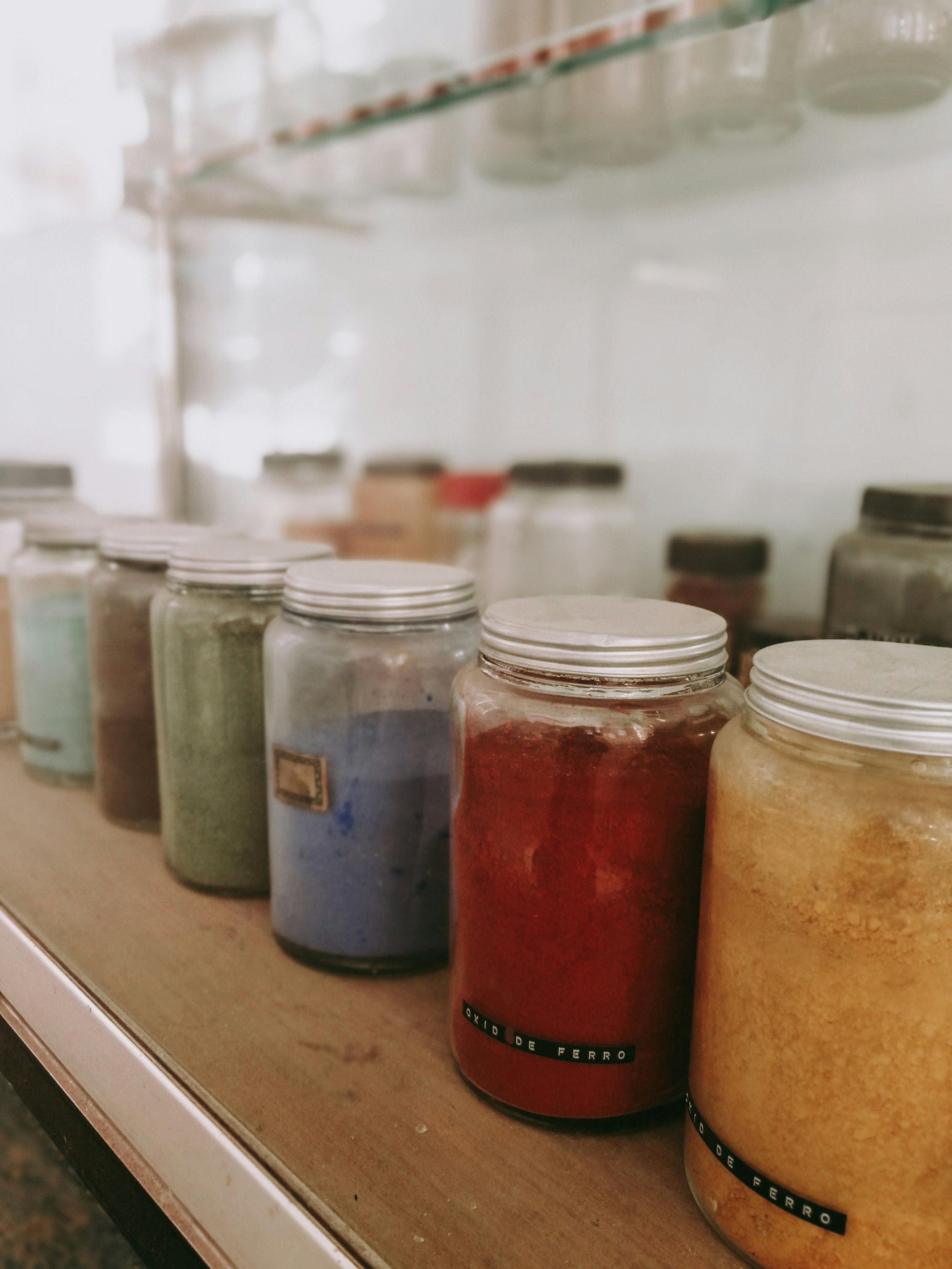
Plant and earth-based dyes are natural colorants derived from botanical, mineral, and biological sources. In 2025, they have reached a "renaissance" as a vital sustainable alternative to synthetic colorants, which are responsible for approximately 20% of global industrial water pollution.
I. 2025 Market & Economic Importance
The global natural dyes and pigments market is valued at approximately $5.07 billion to $5.36 billion in 2025.
Dominant Regions: The Asia-Pacific region maintains the largest market share (over 70% in 2024), driven by vast raw material availability in countries like India and China.
Growth Drivers: Increased regulatory pressure, such as the EU's "Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability," and rising consumer demand for "clean-label" products in fashion and cosmetics are fueling a projected annual growth rate of roughly 6%.
Agricultural Impact: Cultivating dye plants like madder can be at least four times more profitable than traditional cereal crops. In 2025, these crops are being used to revitalize barren or infertile land, supporting rural economic stability.
II. Importance for Cultivation & Sustainability
Natural dyes promote a "regenerative" approach to agriculture and industry:
Zero-Waste Systems: Many dye sources are derived from agro-industrial waste, such as spent coffee grounds, onion skins, or pomegranate rinds.
Resource Efficiency: Natural dyeing processes can reduce water consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional synthetic methods.
Biodiversity: Cultivating a variety of indigenous dye plants supports local ecosystems and prevents the monoculture-dependency seen in synthetic chemical production.
III. Artistic Aesthetic & Symbolism
The "art" of natural dyeing is defined by its unique sensory and cultural qualities:
Visual Complexity: Unlike the flat, uniform colors of synthetic dyes, natural colorants are "alive." They contain multiple dye compounds that react differently to soil, climate, and pH, creating rich, subtle tones that are impossible to replicate perfectly.
Tactility and Sensory Experience: Naturally dyed textiles often retain the soft, aromatic qualities of their source plants, contributing to "biophilic" interior designs that reconnect humans with the natural world.
Cultural Heritage: Reviving traditional techniques—such as West African plant dyeing or Provencal madder cultivation—protects ancestral knowledge and elevates each piece of work into a "living history".